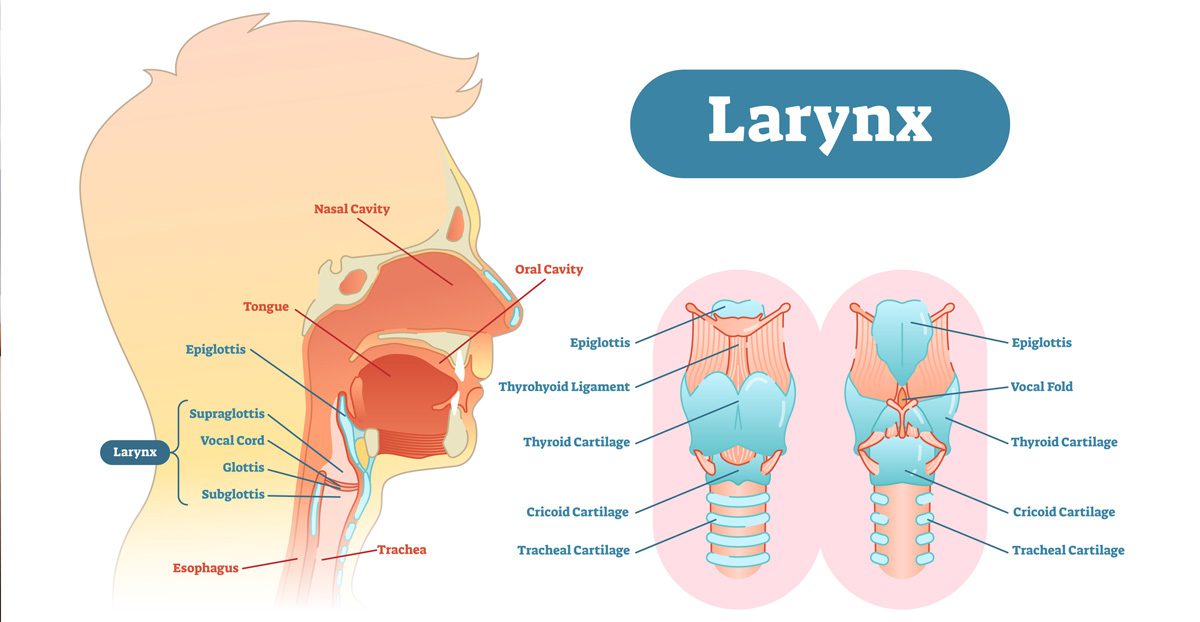
Voice, an essential tool for communication, is produced when air from the lungs is pushed through the vocal cords, causing them to vibrate and produce sound. However, various issues can affect the vocal cords or the voice box, leading to voice disorders. These conditions can significantly influence a person’s quality of life, impacting both personal and professional interactions.
Overview of Voice Disorders
Voice disorders can result from various factors, including physical, neurological, or environmental causes. They can manifest as changes in pitch, volume, or quality of voice. Some people might experience hoarseness, while others may notice breathiness or a complete loss of voice.
Common voice disorders include:
- Vocal Cord Nodules and Polyps: Benign growths on the vocal cords caused by overuse or misuse of the voice.
- Vocal Cord Paralysis: A condition where one or both vocal cords don’t open or close correctly, often due to nerve damage.
- Laryngitis: Inflammation of the voice box, commonly due to infections, irritants, or overuse.
- Spasmodic Dysphonia: A neurological disorder causing involuntary spasms in the muscles of the voice box.
- Reflux Laryngitis: Irritation of the voice box due to acid reflux.
- Laryngeal Cancer: Malignant tumors in the voice box.
Symptoms
Voice disorders present a range of symptoms, which can vary based on the underlying cause. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Hoarseness or roughness in the voice.
- Breathy or weak voice.
- Frequent throat clearing.
- Pitch breaks or inability to reach high notes while singing.
- Pain or discomfort while speaking.
- Loss of voice.
Causes and Risk Factors
Voice disorders can be attributed to a multitude of causes.
- Misuse or overuse: Habitual yelling, whispering, or coughing can strain the vocal cords.
- Infections: Viral or bacterial infections can lead to inflammation of the voice box.
- Neurological conditions: Diseases such as Parkinson’s or multiple sclerosis can affect voice quality.
- Growths: Benign or malignant growths on the vocal cords can lead to voice changes.
- Surgery or injury: Damage to the voice box or nerves can result from surgeries or traumatic injuries.
- Environmental factors: Allergens, pollutants, or chemicals can irritate the voice box.
- Reflux: Stomach acids reaching the throat can cause inflammation of the vocal cords.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Accurate diagnosis of voice disorders often requires a comprehensive approach:
- Physical Examination: This involves visually inspecting the throat and neck.
- Laryngoscopy: A procedure where a thin, flexible tube with a light is used to view the voice box.
- Voice Assessment: Evaluating pitch, loudness, and quality of the voice.
- Stroboscopy: Using a strobe light to watch the vocal cords’ movement during speech.
Treatment options are determined based on the specific disorder and its severity:
- Voice therapy: Working with a speech-language pathologist can help improve voice habits and techniques.
- Medication: Drugs can be prescribed for conditions like reflux laryngitis or infections.
- Surgery: In the case of growths or certain structural issues, surgery might be necessary.
- Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding irritants, staying hydrated, and not smoking can aid in recovery and prevention.
With the advances in diagnostic tools and therapeutic techniques, most voice disorders are treatable, ensuring individuals can regain their voice and continue with their daily interactions confidently. Protecting one’s voice by avoiding strain, staying hydrated, and being conscious of environmental irritants is essential for maintaining vocal health.
